Managerial Issues of IT
Managerial Issues of IT
The usage of technology brings about several challenges as people begin to discover how technology can be of help to them in their own personal way. The relationship between technology and the society is a very interseting phenomenon. To understand this we have to look at the whole thing in two different ways.
First, as said in an old adage, “Necessity is the mother of invention”. People in a given social setting face challenges to their living style and this challenge provokes them to discover and/or invent new tools and techniques which give them the opportunity to bring about the necessary change in their onw life styles. For example, writing was proving to be a pretty difficult task and was error prone and so the printing press was born. Same way, moving things from location to location was difficult and so the wheel was born. Name a noteworthy invention or discovery, it was done by someone who tried ot solve a specific problem related to or associated with a social life style.
Second, as people put to use the technology, it shapes their life styles. That is different people use the technology for different purposes and as the scope of its usage widens, the technology evolves and goes through iterations that were probably not even been thought of by those that invented it in the first place. The potter might have invented the wheel for making his potter's life easy. Someone took it and built a cart and carried things around with ease and grace. Someone else tied a horse to it and made it into a fast moving vehicle, someone else gave it to a kind and made him fight differently, and someone else built a roller skate, and the story goes on.
Sot the impact of technology is two fold. First, the society initiates the building of technology and hence the technology would be shaped initially by a social need. Then as the technology is put to use in a given community, it shapes the way the community is structured and as its adoption grows in scale it becomes central and influential for the existence of a certain kind of life-style.
Having said this, let us now examine what Managerial issues are present in the usage of Information Technology. Suffice it to say here that it was business that actually grew the need for information technology and nurtured that demand for quite a while and now the same technology is shaping the way business is carried out and the evolution of the digital firm.
Managerial Issues of IT
A. Ethical and Security Challenges
There are many ethical and security challenges of having information online. We shall see them in a separate session dedicated for the same.
A. Managing the Structural Changes
IT brings strucutral changes as organization structures, job roles and job descriptions change with the introduction of and wide spread adoption of IT
A. Managing the IT Function
The IT Function is a speacialized function that helps the organization built, operate and maintain the techonological base that it needs to run its business. From one person division for small businesses to a completely functional team of several hundreds in multinationals we will see which aspects of managing the function require attention and which garner lesser interest.
Managing Structural Changes
1. Organization Structure Changes with the use of IT: The usage of IT, as we have seen earlier can either reduce labor cost at the lowest echelons by heavy automation and at the higher levels can replace managerial work. Thus, when less people are required, the nature of the
organization and the strucutre that represents how the organization is governed undergoes a change. What we mean by structural change is the change that is seen in the authority – responsibility relationships that people share.
(a) When the span of control increases, the organization is expected to become flat. There are two consequences of this structural change
i. The speed at which communication reaches the top management becomes very fast.
Thus we can see most people at the top levels of management experiencing a flood of information coming their way. Unless executives are trained to handle this information overload, it becomes a burden and an unwanted intervention. However, the top management being known as closeby and approachable is a definite plus.
ii. People would end up spending more time on email, tele conferences and other impersonal or semi personal forms of communication. This leads to a feeling of not being personally in touch in many cases. However, people can be trained to handle this psychological side effects and be able to manage their teams better with the help of technology than without its help.
2. Roles and Job Descriptions go through a change
(a) The jobs of people, how they report, what they do, how they do whatever they are doing, how they manage people, how they impact others with their communication, everything undergoes a change and this finally requires a change in the role and the job description of many people in the organization. The digital firm requires someone who is not only trained in technology, but also trained in handling the socio-cultural issues that crop up during the period.
3. Managing the learning curve
(a) People need to constantly learn and upgrade. The more technology is being shaped by our needs, the more it will shape us and our needs further. Thus, learning is a continuous
process in digital firms, and learning curves of the people must be given adequate attention. Slow learners might turn out to be detrimental to the system, which quick adapation would require frequent upgrades to newer and better models of IT for organizations.
Managing Structural Changes
A. Managing the resistance to all these changes
One thing which is taken for granted, which will probably seldom change, is change itself. And when things change people are not going to embrace it with open hands. There is going to be resistance to change. Usually, people do not embrace that change which requires them to make an alteration in their context of life itself. IT is a powerful change in peoples life and it demands that people think and act fundamentally differently. Thus, one can expect that there would be a great deal of resistance to this change. Managing the resistance is a very major issue in organizations
Those who are tech savvy suddenly embrace change and would be seen as power usurpers and would be hated by those who held power earlier. This way of looking at things is detrimental to the progress that the technology can bring.
Those who resist changes in IT being sought after by top management are usually looked upon as rebels and conservationalists. But, they also may be those whose contributions have been key to the success of the organization. Thus identifiying those who are resisting change, finding out their reasons for resistance and giving them time and space for a change are the usual tactics that need to be followed.
A. Formulating the Information Policy
Information policy is the policy that determines who gets what information and how that information can be used by different groups of people in the organization. It consists of the following Parts Access Rights: Who accesses which information at what point in time? Who is the one who has authorized them to see that information? Which information is wanted, and how long it is required? What will be done with the information once it is accessed and processed? What are the outputs required and why this information input is needed to produce the output? These are some of the questions that are asked before granting the access to information which is not within the direct scope of the seeker.
Disclosure
Information can be protected, but it must also be disclosed to the right people at the right time so that decisions are made effectively. Also concealing information, even unintentionally, leads to lack of trust. Thus to build trust amongst employees, customers and suppliers, sufficient disclosure of information must be there. At the same time the disclosure should not lead to any advantage to any singly group such that the other groups are victimized.
Distribution and Usage
Where the information is flowing? Whether it is allowed to have free flow or not? Whether the usage is permitted or not? How can the usage be done such that enough information is disclosed but enough is concealed from competitiors? Such are the challenges being faced by professionals and IT practitioners when it comes to distribution and usage of information.
Privacy of customer and employee information is a very critical aspect. Customer databases, and vendo databases are usually very attractive sources of income if one decides to sell them for a profit. However, such distribution of information leads to lack of trust between all the three parties. This makes the job of information collection much more difficult. That is to say that people will not be interested in revealing any information as they would find that its usage is not appropriate.
Managing the IT Function
A. IT function is usually outsourced
Sometimes its cheaper, easier and efficient to let someone else who is good at managing the IT function manage it for the organization. The core business of the organization, in that case, gets more time and attention than the supportive function and hence the outsourcing option is looked at.
A. Managing the interfacing between the IT Solution Provider and the organization
It requires a special interface to manage an outsourced function. The business to which this function is outsourced might not be in complete alignment with the organizations mission and goals. Hence it would require special attention and wise interfacing
A. Managing the dependency on the technology
Too much dependence on a given technology will lock down the firm to a few vendors and therefore, probably might compromise the firm's goals and objectives. Thus care must be taken to have alternative technology plans and crisis management plans when things are not working out and the vendor of IT is being manipulative.
The Internet: Evolution and Revolution Basics of doing business on Internet
The Internet: Evolution and Revolution
The Internet actually began its journey in the late 1960s as an experiment by the military and a few academic researchers called DARPA. In fact four computers were connected in the experiment to see how information could be exchanged over them in real time. This experiment's success lead to an expansion in connecting many computers, especially in the academic community as they could exchange research based information without doing much of travel. Thus began the utility of having connected computers. However this revolution was slow. Once Business Enterprises saw the utility of such networks, the whole scenario turned out to be different.
The early 1980s saw an increase in the number of Internet hosts being available as businesses started to create networks which are accessible, not only to their employees, but also to their customers and vendors. As time passed by, we can see that an almost vertical growth took place in the number of hosts and by the early 1990s, the Internet amongst the business community was a well established phenomenon. What is noteworthy is the amount of technological innovations that happened around this phenomenon. Ability to connect devices manufactured by a variety of hardware companies, standardized way of producing devices such that they are compatible with each other, establishing, refining and implementing different protocols for reliable communhication delivery, developing the ability to handle various types of data in an effective manner, etc., laid out the foundation for the ultimate network of networks called the Internet.
After the 1990s the Internet through the World Wide Web became a common phenomenon even in the households. Avaialability of information that is useful for everyone, cheaper, faster and better devices such as personal computers, mobile phones, etc., helped to accelerate this phenomenon. Thus, we can see that the outreach of the network in terms of hosts available and in terms of number of hits each host was receiving is pretty vast. This could not have been achieved if the above stated supplimentary phenomenon have not happened, when they had to happen.
Revolution!!
Revolution is when a large set of people start to fundamentally THINK AND ACT differently from the normal and accepted ways of thought and action.
The availability of information on line whenever and wherever needed, the ability to connect to the Internet whenever and wherever needed enormously altered the way of thinking people had about their work and personal life. Availability of connectivity on demand helped business to think of new ways of interacting and engaging customers, vendors and employees.
Hence we can see that the Internet did bring about a Revolution to the very fundamental way people lead their lives.
The Internet Revolution
A. New ways of communicating and connecting with people Telephone Vs Email Vs Social Networking: As information started travelling faster than humans can travel and as information could be organize in a personalized form that aided the understanding of the individual, more new ways of communicating and connecting with people started emerging. Telephones and then emails and then social networks made it possible not only to inform people about the businesses, but also to engage them in a variety of activities, collect feedback and analyze it for effectiveness. Hence a whole new way of delivering business results opened up because of Internet
A. Access to information
Information, Knowledge, Discovery&Invention: Its not only about accessing of information, but also about processing it in different ways, to suit different situations and thinking styles, quickly and effectively that leads to Knowledge, Discovery and Invention. The Internet, with its ability to cut across communication channels, networks and data types enabled people not only to access information, but also to process them and personalize them in ways that suited their tastes and preferences. The result of such processing can now be shared, re-analyzed and re-shared. This ability leads to knowledge and discovery and invention.
4. The Internet Business Models
(a) B-2-C E-commerce: Also known as Business to Consumer sites. These sites allow customers to browse for information, place enquiries and orders, engage in conversations and pay through several online methods
i. Flipkart
(b) B-2-B Exchanges: Also known as business to business sites. These sites allow vendors and suppliers to exchange information with each other.
i. FedEx
(c) B-2-G: Business to Government sites. Allows a business to connect to a governing and/or regulatory body seemlessly and interact with them on several policy related matters.
i. E-Governance
(d) C-2-C: Customer to Customer sites. Sites built by organization where customers get to know other customers, and engage in active discussions on their needs and wants.
i. Wikipedia, Facebook An Example
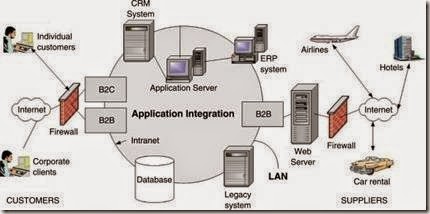
Given below is a self-explanatory diagram of how the above business models fit into an enterprise system. As we ca nsee B2B and B2C models, different types of networks can be integrated to suit the needs of the business strategy.
Information Flows
The Diagram below refers to the hard product flows and the information flows throughout the supply chain beginning from the suppliers and ending with customers. The Solid Red lines are the hard products, the dotted red lines are soft information products, the dotted blue lines are orders and payment flows. One thing that is clearly evident from the diagram below is that the pace at which business can be carried out is now the pace at which the hard product can be moved from the supplier end to the customer end. The soft and information products from no real barriers as their speeds are independent of and faster than the speed at which the hard products move.

Five key components of running a business
A. Location and Hosting
Traffic: The location and hosting depends on the size of traffic expected.
Image: Different hosting services ranging from free hosting to exclusive and customized hosting are available. While free hosting requires you to ride on someone else's website
name, it gives you access to be present on the Internet, exclusing and customized hosting is often flexible and expensive. Choosing the host with an appropriate image is critical
for the Internet business to be successful or not.
Competition: Number of players being hosted in a given location and the traffic spread across the players is also a noteworthy factor
Convenience: How quickly and easily can the information be presented to the customer and how flexible can it get when it has to be presented across different gadgets.
Size
Bandwidth, Processing Power, Data Storage: The size of information and the amount
of information transfer per unit of time will determine what are the requirements for bandwidth, processing power and data storage.
Domain name registration
This is often cumbersome as many domain names (the website name) are already taken and one might have to pay for the name registration service. Hosting Free hosting: Some service providers offer free hosting services. Usually experimental startups and people who do business at a very fundamental level use these services. Usually they are very limted and do not allow complex e commerce transactions to take place.
Shared Server hosting: Several people share the server, but the domain names will be unique. However, the amount of space available will be limited. If competing websites are sharing the same space, then possible security threats are many.
Dedicated Servers hosting: Dedicated servers are host computers that are exclusively given for the use of the e-commerce business. The whole of the data and software is exclusively of the domain holder and greatest felxibility is available here.
Co-Located Servers: Servers located in large and unique infrastructural setting that enables the servers to perform better and cheaper are called co-located servers. By sharing infrastructural facilities the cost of the server and the service comes drastically down.
In-house hosting: Organizations own hosting without depending on a third party hosting service is called in house hosting. This type of hosting is preferred either if there are high level security concerns and/or when the organization wants to have everything under their control.
A.Marketing and Presentation
Next task is to attract and retain customers through a variety of awareness-building activities
Advertising: A traditional way of getting attention from customers. Different print and electronic media are avaialble for the same.
Guerilla Marketing: Its a technique of hiding the marketing effort till the last minute and unleashing a plethora of activities that can take the competion by surprise. The following are some of the characteristics
Characteristics of Guerilla Marketing (Traditional & Web-based)
A. It does not include overt media buys. That is media buying is kept secret.
A. It relies heavily on word-of-mouth to spread its message. The competition cannot sense it as it is informal communication
A. It is generally used by companies with limited budget. Its cheaper and requires a
special talent to use informal and non-traditional wasy to attract customer attention.
Additional Web-based Techniques
A. Affiliate Programs – Marketing programs designed to enable merchants to mobilize other websites (affiliates) to help sell products, produce traffic, or build brand
A. Viral Marketing – Company-developed products, services or information that are passed from user to user Direct Marketing
A. Involves direct contact between the company selling a product or service and the intended customer
A. ften considered intrusive and annoying
A. Examples of direct marketing:
e-commerce: Unsolicited email (“spam”), newsgroup postings, etc.
A. Presentation
In addition to traditional advertising methods, e-commerce can use Web-based marketing efforts
Search Engine and Directory Listings
A. Search Engine Optimization: The process through which a website can make itself appear in the top ten list presented by various search engines. This can be easily done by knowing how search engines evaluate information being presented on a website and place a rank on relevance of the site to the seeker of information
A. Paid Placement : Sponsored placements where the advertisement appears at a
preferred spot such as on the top of the webpage etc.,
Banner Adds
A. Most common advertising product on the Web
A. Can be highly Targeted: Can be displayed to only those customers who are actively seeking information.
A.presentation
Presentation serves to add or detract from product’s appeal to customer. It helps to draw and retain customers to a store
Aspects of Online Presentation
User Interface: It is a very critical aspect of any e-commerce business
A.s the e-commerce equivalent of Store Layout for brick-and-mortar stores
A. Should reflect the theme of the store represented, be easy to navigate, and be pleasing and viewable to the store’s customers
Information Access (database navigastion)
Website should be fast and easy to navigate. Usually when information from a database has to be retrieved and processed to fit into the user's needs, it takes a long time to interact with a database service. This was so earlier because the data services were not an integral part of the world wide web. As business enterprises started using the web, these services became important and today are an integral part of any web based application development tool
Customer Service
Defines the customer’s experience
It is a leading driver of customer retention
e-commerce does not allow for real person-to-person live interaction
A. Payment
Cash-on-Delivery Models: This delivery model is very critical in India as it avoids on- line payment. The reason this model is popular is because of two reasons. First, the reach of credit cards and the internet payment gateways is very limited and the businesses expand byond this reach. Second, there is a lot of insecurity associated with online
payments in terms of cyber theft and cyber crime. Hence this is a preferred mode of
payment.
On-Line Payment Models
Credit Cards / Debit Cards: submitting account and card information so that the website can access the bank's website and do an online transfer of money.
PayPal: A peer-to-peer payment system in which bank account and electronic transfer of money is handled completely by a third-party and the rest of the exchange
happens through emails.
Mobile Payments: Same as credit cards, but payments are done through a mobile phone rather than through a credit/card
A. Security
e-commerce stores require more sophisticated and technologically complex security measures
Attacks can potentially come from a worldwide base of hackers Potential for damage in the event of attack is much greater
A. Fulfillment
Fulfillment encompasses all activities that enable merchants to complete customer orders It is a significant factor in determining profitability of an e-commerce venture
For e-commerce, fulfillment is similar to that of catalog sales Burden of delivery is placed solely on merchant Challenges of e-commerce fulfillment
Customer demand for Transparency
A. Providing increased information demand from Web customers requires seamless integration of different systems and information sources
Multiple Activities and Parties
A. Must be capable of handling many activities and parties simultaneously
Multiple Systems
Must be able to coordinate between different platforms and computer systems
Capacity Utilization
Must be able to accommodate fulfillment during peak times and yet have efficient capacity utilization during valleys. This can be accomplished by outsourcing fulfillment to third party e-commerce service providers (ESP)




Comments
Post a Comment