e-Business and e- Commerce:e-Business systems,e-commerce systems and Essential e- commerce processes.
6.1e-Business systems
E-Business refers to the use of digital technology and the internet to execute the major business processes in the enterprise. e- Business includes activities for the internal management of the firm and for coordination with suppliers and other business partners. e-business is the use of the internet and other networks and Information Technologies to support e-commerce, enterprise communications and collaboration both within a networked enterprise and with its customer and business partners. e–business includes e-commerce, which involves the buying and selling and marketing and servicing of products, services and information over the internet and other networks.
6.2e-commerce systems
Electronic commerce encompasses the entire online process of developing, marketing, selling, delivering, servicing, and paying for products and services transacted on internetworked, global marketplaces of customers, with the support of a worldwide network of business partners. Electronic commerce is more than just buying and selling products online. It is the Process of buying, selling, transferring, or exchanging products, information and services through computer networks. It uses Internet and Web to transact business. The fundamental purpose of e-commerce is to execute digitally enabled transactions. It allows a business of virtually any size that is located virtually anywhere on the planet to conduct business with anyone, anywhere. It allows geophysical barriers to disappear, making all consumers as potential customers.
Fig 6.1 represents the range of business processes involved in the marketing, buying, selling and servicing of products and services in companies that engage in e-commerce. Companies involved in e-commerce as either buyers or sellers rely on Internet-based technologies and e-commerce applications and services to accomplish marketing, discovery, transaction processing, and product and customer service processes. Electronic commerce systems rely on the resources of the Internet, intranets, extranets, and other computer networks. Electronic commerce can include:
• Interactive marketing, ordering, payment, and customer support processes at e-commerce sites on the World Wide Web
• Extranet access of inventory databases by customers and suppliers
• Intranet access of customer relationship management systems by sales and customer service reps
• Customer collaboration in product development via Internet newsgroups and E-mail exchanges
Why e-commerce is different
• Ubiquity- available everywhere at all times
• Global Reach- potential market size for e-commerce is roughly equal to the size of the world’s online population
• Universal cost- technical standards for conducting e-commerce are universal standards
• Richness(Information)- Web makes it possible to deliver rich messages with text, audio and video simultaneously to large number of people
• Interactivity – allows two way communication
• Information Density - total amount and quality of information
• Personalization/Customisation – messages to a person’s name, interests and past purchases
Digital Market compared to Traditional Market
Categories of e-Commerce
The Internet, intranets, and extranets provide vital electronic commerce links between the components of a business and its customers, suppliers, and other business partners. This allows companies to engage in three basic categories of electronic commerce applications:
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) – businesses develop attractive electronic marketplaces to sell products and services to consumers. Companies may offer:
• e-commerce websites that provide virtual storefronts and multimedia catalogs
• Interactive order processing
• Secure electronic payment systems
• Online customer support
Eg: Retailing, Online reservations
Business-to-Business (B2B) – involves both electronic business marketplaces and direct market links between businesses. Companies may offer:
• Secure Internet or extranet e-commerce websites for their business customers and suppliers
• Electronic data interchange (EDI) via the Internet or extranets for computer-to-computer exchange of e-commerce documents with their larger business customers and suppliers
• B2B e-commerce portals that provide auction and exchange markets for businesses. eg:Boomi.com- Addresses information, knowledge and business requirements of various players
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) -Successes of online auctions like e-Bay, allow consumers (and businesses) to buy and sell with each other in an auction process at an auction website.
• Sponsoring consumer or business auctions are an important e-commerce alternative for B2C or B2B e-commerce
• Electronic personal advertising of products or services to buy or sell by consumers at electronic newspaper sites, consumer e-commerce portals, or personal websites is an important form of C2C e-commerce.
eg: Ebay.com-web auction site
6.3 Essential e- commerce processes
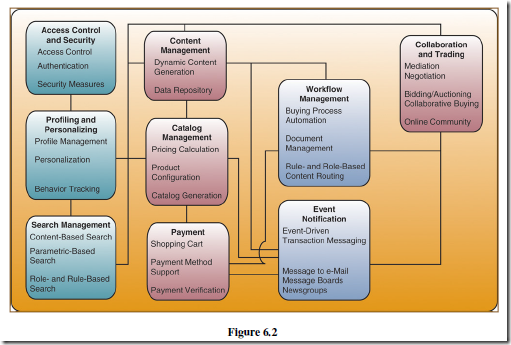
The nine essential e-commerce processes required for the successful operation or management of e-commerce activities consist of:
• Access control and security
• Profiling and personalizing
• Search management
• Content management
• Catalog management
• Payment
• Workflow management
• Event notification
• Collaboration and trading
Access Control and Security
E-commerce processes must establish mutual trust and secure access between the parties in an e- commerce transaction by authenticating users, authorizing access, and enforcing security features. For example customer can access any e-Commerce site only through user names and passwords, encryption keys or digital certificates and signatures. The e-commerce site can also authorise access to only those parts of the site that an individual user needs to accomplish the transaction.
Profiling and Personalization
Profiling processes gather data on an individual and their website behaviour and choices, and build electronic profiles of their characteristics and preferences. User profiles are developed using profiling tools such as user registration, cookie files, website behaviour tracking software, and user feedback. Profiling processes are also used to help authenticate identity for account management and payment purposes and gather data for customer relationship management.
Search Management
Efficient and effective search processes provide a top e-commerce website capability that helps customers find the specific product or service they want to evaluate or buy. e-commerce software packages can include a web site search engine component.
Content and Catalog Management
Content management software helps e-commerce companies develop, generate, deliver, update, and archive text data, and multimedia information at e-commerce websites. E-commerce content frequently takes the form of multimedia catalogs of product information. Generating and managing catalog content is a major subset of content management.
Content and catalog management may be expanded to include product configuration processes that support Web-based customer self—service and the mass customization of a company’s products. Configuration software helps online customers select the optimum feasible set of product features that can be included in a finished product.
Workflow Management
E-business workflow systems help employees electronically collaborate to accomplish structured work tasks within knowledge-based business processes. Workflow management in both e-business and e- commerce depends on a workflow software engine containing software models of the business processes to be accomplished. The workflow model expresses the predefined sets of business rules, roles of stakeholders, authorization requirements, routing alternatives, databases used, and sequence of tasks required for each e-commerce process. Workflow systems ensure that the proper transactions, decisions and work activities are performed.
Event Notification
Most e-commerce applications are event-driven systems that respond to a multitude of events. Event notification processes play an important role in e-commerce systems, since customers, suppliers, employees, and other stakeholders must be notified of all events that might affect their status in a transaction. For example when a customer purchases a product from a retail website, they receive an e- mail record of the order. The customer may also receive an e-mail notification of change in product availability or shipment status and finally an e-mail message is received notifying about the shipped product.
Collaboration and Trading
This category of e-commerce processes are those that support the vital collaboration arrangements and trading services needed by customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders to accomplish e-commerce transactions.






Comments
Post a Comment