FUNDATIONS OF INFORMATION SYSTEMS PART2
7 Contributions of IT that makes a difference to the success of a business
Three important reasons why IT makes a difference to the success of a business are mentioned below.
1. Foundation of doing business
2. Productivity
3. Strategic opportunity and advantage
7.1. Foundation of doing business
Most businesses today could not operate without extensive use of information systems and technologies. The organizations more specifically using e-commerce and e-business like Amazon.com, e-bay, wall-mart and such organizations would have not exist without IT. IT can help a business become a high-quality, low-cost producer and hence to increase market share. IT is vital to the development of new products.
There is a growing interdependence between a firm’s information systems and its business capabilities. Changes in strategy, rules, and business processes increasingly require changes in hardware, software, databases, and telecommunications. Often, what the organization would like to do depends on what its systems will permit it to do.
Down the line five years the firm’s strategic growth and profit level depends on how the company implements the IT and build the IT capabilities in the firm and hence IT acts as a Interdependence between Organizations and Information Systems. This Interdependence between Organizations and Information Systems is presented in figure 1.7.
Figure 1.7.Interdependence between Organizations and Information Systems
7.2. Productivity
IT is one of the most important tools manager’s uses to have increase productivity and efficiency of businesses. IT is a major factor in reducing costs. For firms, IT is a major source of labor and capital efficiency.
7.3. Strategic Opportunity and Advantage.
Information technology creates strategic opportunity and advantage to business organization. But the kind of getting the competitive advantage depends on the organizations’ capability to use IT and its innovation as uniqueness in their business. Although, IT is available in the market, and immitigable by the competitors but still the organizations’ capability to use IT matters more.
E.g. Dell Computers, Amazon, e-bay, Google are the some examples of the global organizations which adopted it and innovations to their business and gained competitive advantages in the market.
Further, Strategic Opportunity and Advantage may be viewed with following points.
• Create competitive advantage: IT makes it possible to develop competitive advantages.
• New Business Models: Dell Computer has built its competitive advantage on an IT enabled build-to-order business model that other firms have not been able to imitate.
• Create new services: IT makes it possible to develop Create and develop new services. E.g. E Bay has developed the largest auction trading platform for millions of individuals and businesses.
• Differentiate the organization from the competitors: IT and its innovation may be adopted as uniqueness in their business to differentiate the organization from the competitors. Amazon has become the largest book retailer in the United States on the strength of its huge online inventory and recommender system. Amazon, eBay, Dell, Wal-Mart and Apple's iTunes are just a few firms that have built and maintained technology-based advantages.
8 Impact of IT in business firms
There are five factors to consider when assessing the growing impact of IT in business firm. They are mentioned below.
1. Internet growth and technology Convergence.
2. Transformation of Business Enterprises.
3. Growth of a globally connected economy (Globalization).
4. Growth of knowledge and information-based economies
5. Emergence of the digital firm
Further, above impacts are discussed briefly in the below sections.
8.1. The Internet and Technology Convergence
Internet is bringing about rapid changes in markets and market structure: financial services and banking such as eTrade.com. Internet resulted growth in e-business, e- commerce, and e-government. The Internet is not emerged and burst but it will continue to be a flat form to do the business. The Internet is making many traditional business models obsolete.
8.2 Transformation of Business Enterprises.
Along with rapid changes in markets and competitive advantages are changes in the firm themselves. The internet and new markets are changing the cost and revenue structure of the traditional firms and are hastening the demise of traditional business models. In addition to the above some more transformations are also caused due to the technological convergence in the traditional business in terms of its structure, management, technology adoption etc. These transformations are presented in the encapsulated manner below.
• Organizations are becoming Flattening
• Organizations are becoming Decentralization
• Organizations are becoming Flexibility
• Location independence
• Low transaction and coordination costs
• Empowerment
• Collaborative work and teamwork
8.3 Globalization
Globalization results various organizations to distribute core business functions in product design, manufacturing, finance and customer supports to locations in other countries where the work may be performed cost effectively. The Globalization leads the management and control in a global marketplace, competition in world markets, global workgroups and global delivery systems which essentially based on digital technology.
8.4 Rise of the Information Economy
Today’s country economy is not only dependent on manufacturing sectors business but also on Knowledge and information-based products. Knowledge and information provides more value the new products and services. In Knowledge and information- based economies, the firms capability and market value will be assessed on new products and services launched by the firm and firm’s Knowledge as a central productive and strategic asset.
8.5 The Emerging Digital Firm
A digital firm is one in which nearly all of the organisation’s significant business relationships with customers, suppliers and employees are digitally enabled and mediated. Core business which involve set of logically related tasks and behaviours that organisations develop over time to produce specific business results and the unique manner are organised and coordinated. Core processes are accomplished through digital networks spanning the entire organisation or linking multiple organisations. In a digital firm, any piece of information required to support key business decisions is available at any time and any where in the firm. Key Corporate Assets of digital firm are Intellectual property, core competencies, and financial and human assets – are managed through digital means. A frame work of Digital Firm is presented in Figure 1.8.
Figure 1.8. A frame work of Digital Firm
8.51 Key benefits of digital firms may be listed as below.
1. They sense and respond to the changing business environments more rapidly than traditional firms, giving them flexibility to survive in turbulent times.
2. The firms offer extraordinary opportunities for more flexible global organisation and management.
3. Time shifting (business being conducted 24x7) and space shifting (business being conducted globally or beyond traditional geographic boundaries) are the norms in the organisations.
8.52 The characteristics of digital firm
A digital firm usually possess the flowing characteristics.
1. Digitally enabled relationships with customers, suppliers, and employees
2. Core business processes accomplished using digital networks
3. Digital management of key corporate assets
4. Agile sensing and responding to environmental changes
5. Seamless flow of information within the firm, and with strategic partners
9 Data versus Information
Data consists of raw facts, such as an employee’s name and number of hours worked in week, inventory part numbers. Several types of data can be used to represent to represent these facts which are organized or arranged in a meaningful manner, they become information.
Raw data from a supermarket checkout counter can be processed and organized to produce meaningful information such as the total sales of soap or the total sales revenue from soap for a specific stores or sales territory.
Information
Information can be defined as the data which is organized and presented at a time and place so that the decision maker may take necessary action. Information in other wards is the result/product of processing data. Figure 1.9 illustrates the differences between data and information
Figure 1.9 Differences between data and information
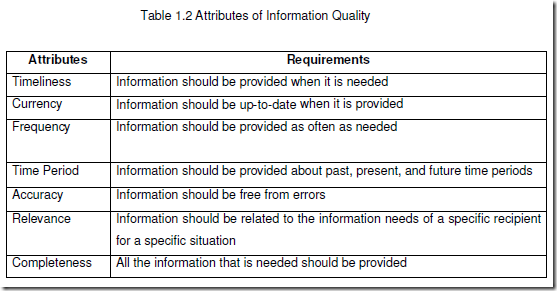
9.1 Attributes of Information Quality
Attributes of Information Quality may be viewed under three important dimensions such as Time Dimension, Content Dimension, and Form dimension. Various attributes along with requirements are furnished in Table 1.2







Comments
Post a Comment